Troubleshooting
In this page you'll learn what are the most common mistakes when implementing the Notificare library for Android.
Enabling debug logging
There are times when the default logging level is not sufficient to diagnose problems. You can enable debug logging by adding the following to the AndroidManifest.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest>
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="re.notifica.debug_logging_enabled"
android:value="true" />
</application>
</manifest>Managing application state
Important application data, such as current device information and push state, is stored in shared preferences.
It's essential to avoid manually removing these properties or files, as doing so can have unintended side effects, essentially resetting your application to a partially fresh state.
Instead, we recommended using the appropriate functions that align with your specific use-case, such as disableRemoteNotifications() or unlaunch().
Misplaced App Keys
When implementing Notificare, the library configuration file (located at app/notificare-services.json) must contain the Application ID, Application Key and the Application Secret.
In Google Cloud Messaging/Firebase Cloud Messaging there is no separation between development and production environment, so you don't necessarily need to create applications in Notificare for both environments, although we strongly recommend that you have an application for each environment.
Please read more about the configuration file here.
GCM/FCM Errors
A very common mistake it to confuse the SenderID with Server Key. There's a clear distinction between the two. They both can be found in the Firebase's Developer Console, like shown here. The SenderID is included in the google-services.json file added by Firebase to your app like explained here.
The Server Key is generated by Firebase and uploaded to Notificare, like shown here. This will enable our platform to send notifications to your app.
Missing Dependencies / Permissions
One of the most common mistakes when implementing Notificare are missing permissions in your AndroidManifest.xml file.
Some of these permissions are required for the library to work. In most cases this will originate crashes when building your application.
Necessary permissions are automatically added by the various Notificare modules, so make sure you include all the dependencies your application will need. You can read more about the dependencies here.
Google Maps key in Android
Notificare will require access to the Android Maps API in order to display Google Maps. These maps can be included in the content of a notification. Most common mistake when using Android Maps is to forget to get access to the API and to generate an Android Key. You can read more about creating an Android Maps V2 Key, here.
Application crash during start-up
Fatal Exception: java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to get provider re.notifica.NotificareConfigurationProvider:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No platform dependencies have been detected. Please include one of the platform-specific packages.There are times when the exception above occurs. Typically, it's due to a misconfiguration.
- Ensure you run your application in a compatible emulator. Since not all images support Google Play, running the app in such emulators will cause the exception since the device doesn't have the necessary capabilities.
When choosing an emulator image, select one that looks like the following.

Known Issue with Moshi in Gradle 8.0
We are aware of an issue with this dependency when built with the latest Android Studio, which includes Gradle 8.0 where R8 is enabled by default. Basically, until they are able to provide a better solution, you need to add the following Proguard rule to your app:
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking class com.squareup.moshi.JsonAdapterGeofencing with the application in background
Android imposes certain limitations on applications running in the background. These restrictions can either be specific to an application (Standby Buckets) or system-wide (Doze Mode), which applies to all applications.
One of the most significant constraints is limited network access. While some background tasks, like logging events to an API, can be postponed until an appropriate window, geofencing triggers require immediate action. For example, sending a push notification with relevant content upon entering or exiting a specific region demands prompt processing.
If you notice missing geofence triggers while the app is in the background, but they function correctly in the foreground, the background limitations are likely the cause.
Here are some strategies to mitigate these issue:
- During testing you may manually exempt the application from battery optimization restrictions. Navigate to App Info > Battery Usage > Allow Background Usage, and set it to Unrestricted. The exact steps may vary depending on your Android version.
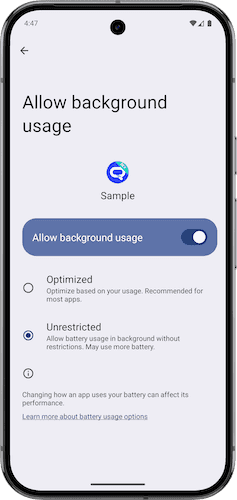
- By using the ACTION_IGNORE_BATTERY_OPTIMIZATION_SETTINGS intent. This intent opens the system settings page controlling which apps can ignore battery optimizations. Be sure to provide explanatory content or a message before invoking this intent to ensure clarity and guide the user.